Mar 12, 2024
Is Your Security Posture Ready for the AI Storm?
Preparing your security posture for the AI Revolution
In the last year, we’ve seen explosive AI growth across various industries, primarily driven by recent advances in generative AI (GenAI) offerings such as ChatGPT. But this rapid AI adoption brings new attack vectors, security and privacy vulnerabilities, and many unknowns.
Security leaders are tasked with adapting strategies, tools, and controls in these unchartered waters as businesses scramble to stay ahead of the AI Tsunami. This requires creative, outside-the-box thinking and a willingness to quickly evolve approaches as new AI-driven services, attack vectors, and security tools emerge. This blog post will provide examples of security challenges we saw in these early days of AI adoption. We’ll also describe Tevora’s approach to helping clients fortify their security posture to address emerging AI threats and requirements.
Unique Security Challenges
Here are a few examples of unique security challenges we’re seeing with the rise of AI:
- When not designed and implemented correctly, Large Language Model (LLM)–based services create new attack surfaces that expose personal information, organizational intellectual property, or other sensitive information.
- Attackers use GenAI tools and public domain knowledge to generate more believable and effective phishing lures.
- Security vendors offer a flood of new tools to address AI-related challenges, many of which still need to be adequately tested. This can significantly strain security organizations as they scramble to research, validate, select, and install these tools.
- Malicious actors manipulate input data to cause AI models to generate incorrect or undesirable outputs.
- Attackers use AI capabilities to automate the discovery and exploitation of vulnerabilities in software and systems.
And these are just the tip of the iceberg.
The Need for an AI Security Program
In many ways, the recent growth in AI reminds us of the early days of cloud adoption. Many security professionals assumed their existing security controls would be adequate for cloud applications but quickly—and often painfully—realized that these controls would not cut it. Please don’t make the same mistake with AI.
You need more than just relying on your current security tools, policies, controls, and processes to protect your organization in an increasingly AI-driven environment. Organizations need a comprehensive security program that addresses the unique challenges of AI.
New GenAI Application Attack Surfaces
Many organizations are rushing to build LLM-based GenAI applications that leverage their data to offer services and insights that ChatGPT or other AI applications cannot provide. Gartner has developed the following summary-level depiction of the new attack surfaces and critical risks that can be introduced with applications like this:
AI Adds New Attack Surfaces to Existing Applications
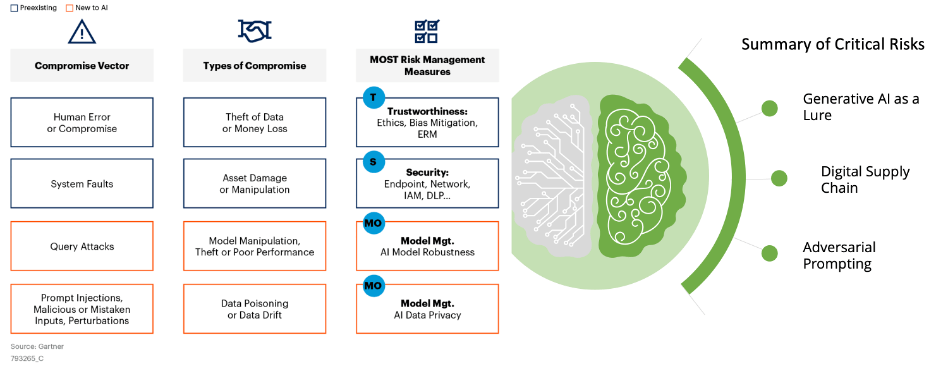
Organizations implementing LLM-based GenAI applications must thoroughly consider these new attack surfaces and risks when developing their AI security programs.
Tevora’s 4-Step AI Security Program
Tevora combines emerging trends with learnings and experience across industries to help organizations implement GenAI securely. Our team of experts uses the following four-step process to help clients develop full lifecycle AI security programs:
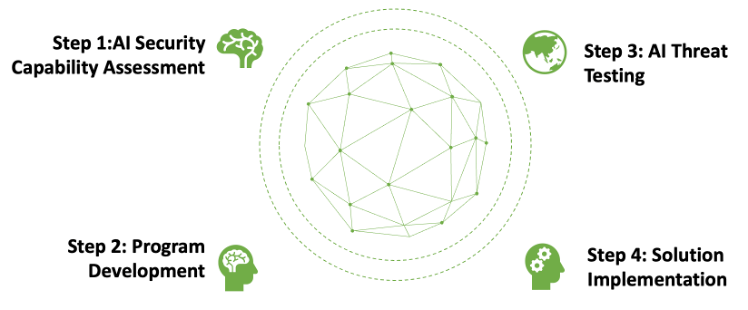
Step 1 – AI Security Capability Assessment
An assessment that evaluates the current organizational usage and capability in AI and LLM, including:
- Define AI Use Cases
- Define Population (users, data, applications)
- Define Data Input and Output from Generative AI tools
- Understand and Identify Risk
- Provide Recommendations for Controls
We can’t stress enough the importance of defining comprehensive AI-specific use cases. Getting this right up front ensures that subsequent steps, such as threat testing and solution implementation, will successfully address AI requirements.
Step 2 – Program Development
Tevora leverages industry frameworks (i.e., NIST, ISO, OWASP), business acumen, and security and risk best practices to develop best-in-industry AI security programs that include the following:
Policies & Procedures
- AI Security Policy
- AI Acceptable Use Policy
- Update of Data Classification/Governance Policy and Procedures
- Update of Risk Assessment Procedure
- Update of Vulnerability Management Policy and Procedure
- Define workflows to inventory, approve, and manage consumptions of GenAI; include “generative AI as a feature”
- Update of Change Control Policy and Procedure
- Third-Party Risk Management
- Update of TPRM Policy and Procedure as new SaaS solutions are added for Generative AI usage (i.e., Microsoft AI, Amazon Lex/Forecast/Comprehend)
- Privacy, Legal, & Compliance
- Identification of any data usage that impacts Privacy Regulations (i.e., General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and upcoming Artificial Intelligence Act), Financial Regulations (NCUA, FFIEC), Legal Requirements (Contracts), and Compliance Requirements (PCI, NIST)
- Update of existing documentation to reflect additional controls and monitoring, depending upon data input and out from Generative AI tools
- User Training—training materials include:
- One-pager cheat sheets
- In-person and online training regarding updated policies and procedures, common threats, and user responsibility
- Technical training for developers regarding API integrations, additional threat testing, etc.
If you will be implementing or currently have an LLM-based GenAI application, it’s critically important to update your data governance program to ensure you won’t feed your AI model incorrect data, which can result in in providing inaccurate information to the model’s users. Your data governance program should also ensure that the model will not inappropriately provide personally identifiable information to model users. Incorporating these considerations in your data governance program will go a long way toward minimizing risks.
Step 3 –Threat Testing
Ensure your organization is secure by testing your defenses before an attacker can exploit any vulnerabilities.
- Test API Integrations
- Intercepting inputs and outputs with a custom-made prompt will improve results and enable more security controls; this type of testing is critical
- Traditional Testing Updated for AI
- Internal, External, and Web Apps; wherever AI or LLM is deployed, our team can design a test for it
- Test Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Larger organizations might investigate prompt augmentation techniques, such as RAG
- Test Private vs. Public Hosting
- Depending upon the implementation, there are different threat vectors that should be pen tested
Comprehensive threat testing is critical for identifying AI-related risks. This will likely require some amount of manual testing. For example, it’s unlikely you’ll be able to just perform an automated vulnerability scan, external audit, or web app audit and call it cooked. Identifying many AI-specific threats, vulnerabilities, and exploits will require manual testing. Over time, automated test tool providers may be able to address more of these AI use cases, but you will likely not find this in the currently available tools.
Step 4 – Solution Implementation
Define requirements and implement tools to monitor or defend against malicious external LLM and Generative AI threats. Tools to consider include, but are not limited to:
- DLP
- UBE/UBA
- Security Service Edge (SSE) providers that can intercept web traffic to known applications
- Web Filtering
- Browser Isolation
We recommend that you use a layered approach to implementing security solutions because current tools are not yet able to fully detect or prevent many AI-powered threats. For example, web filtering tools will likely not be able to detect AI-generated malicious applications that appear to be legitimate. To cover use cases like this, you should take a multi-layered Defense-in-Depth approach, with several independent layers of security controls and solutions so that if one fails, another will work.
Additional Resources
Below are additional resources that provide a deeper dive into the topics covered in this blog post:
- Tevora Datasheet: AI Security Readiness
- Gartner Article: 4 Ways Generative AI Will Impact CISOs and Their Teams
- SentinelOne Blog Post: Purple AI ½Empowering Cybersecurity Analysts with AI-Driven Threat Hunting, Analysis & Response
- Cornell University Paper: Not what you’ve signed up for: Compromising Real-World LLM-Integrated Applications with Indirect Prompt Injection
- Cornell University Paper: Generating Phishing Attacks using ChatGPT
We Can Help
Tevora’s experienced experts can answer any questions about AI and would welcome the opportunity to help strengthen your security posture to be ready for the rising tide of AI adoption. Just give us a call at (833) 292-1609 or email us at sales@tevora.com.